Final Cell Culture
Cell Counting = process of determining cells no 算细胞 importance, method, which method recommended
- importance of cell counting
- ensure accurate seeding densities 播种密度
- monitors growth rates 成长
- evaluates cytotoxicity or proliferation 细胞毒性与增殖
- standardize experimental conditions
- methods
- manual counting
- hemacytometer slide
- requires a minimum of 1x10^6 cells/mL
- use trypan blue for viability test
- viable cells not stained
- cheap
- slow
- prone to error
- low sensitivity
- electronic counting
- original resistance-based counter
- based on the change in current generated when a cell passes through a narrow orifice 孔
- image analysis software
- scan stained & unstained cells in a special counting chamber & view
- continuous monitoring of living cultures
- work by counting cells or determine residual available growth area
- rapid & low inherent 固有 error - more accurate
- needs single cell suspension
- flow cytometry
- count by light scatter, fixed or unfixed cell population or by DNA fluorescent stain
- analyze a single cell stream for cell concentration
- many parameters can be measured simultaneously 同时 - cell size, cell lineage, DNA content, viability (Propidium I), apoptosis (annexin V)
- needs single cell suspension
- technically more complex
- growth curve
- for design experiment - know when to subculture
- population doubling time & cell cycle time determine cell growth
- cell most consistent & ideal for sampling @ log
- cell has altered characteristics @ plateau
- secrete more ECM - more difficult to disaggregate 分解
- saturation density
- density of cells at which the plateau phase is reached
- transformed cells reach higher cell density @ plateau
- higher growth fraction & loss of density limitation
- cell cycle time
- to determine length of cell cycle & its constituent phase
- determined by measuring DNA synthesis
- use bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) = analogue of nucleoside
- BrdU incorporated into replicating DNA, replace thymidine
- DNA-bound BrdU labelled with Ab
- incorporation of BrdU is detected at intervals after labeling by immunofluorescence microscopy/flow cytometry
- for flow cytometry, cells stained with propidium iodide & analyzed for BrdU incorporation vs DNA content
- cell migration
- detailed analysis of time-lapse video sequence
- image analysis of tracks made by the cell's phagocytosis in dishes coated with colloidal gold
- movement of cells thro porous membrane - chemotaxis assay in Boyden chamber/invasion assay in filter well
- data interpretation
- total cells, live cells, dead cells
- doubling time
- population growth curve
- impact of treatment
- tips for accurate counting
- mix cells well b4 sampling
- avoid bubbles in slide
- count consistent squares
- perform in triplicates 三份
- limitations
- subjectivity
- debris
- over or under staining
- calibration for automated counters
Cytotoxicity = quality of being toxic to cells
- cytotoxicity testing = in vitro assay of cell growth, survival, migration, death
- development of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food additives
- humane - reduce animal sacrifice
- economic - cell lines are cheaper
- end point measurement
- cannot predict systemic & physiological effects
- initial screening of compounds
- microtitration assay
- allow screening of large no of samples
- save time & cost
- set up MTT plate
- incubate for 2 population doubling time
- + drug/toxin to cells when cells in exponential growth @ log
- remove drug & allow cells to recover in growth medium
- after 2-3 PDT, remove medium, replace with MTT
- after 3-4h, read on plate reader
- use absorbance plot inhibition curve
- calculate IC50
- nature of assay
- viability
- survival
- metabolic changes
- genotoxicity & transformation
- irritancy
- parameter in survival assay*
- concentration of agent
- invariant 不变 agent concentrations
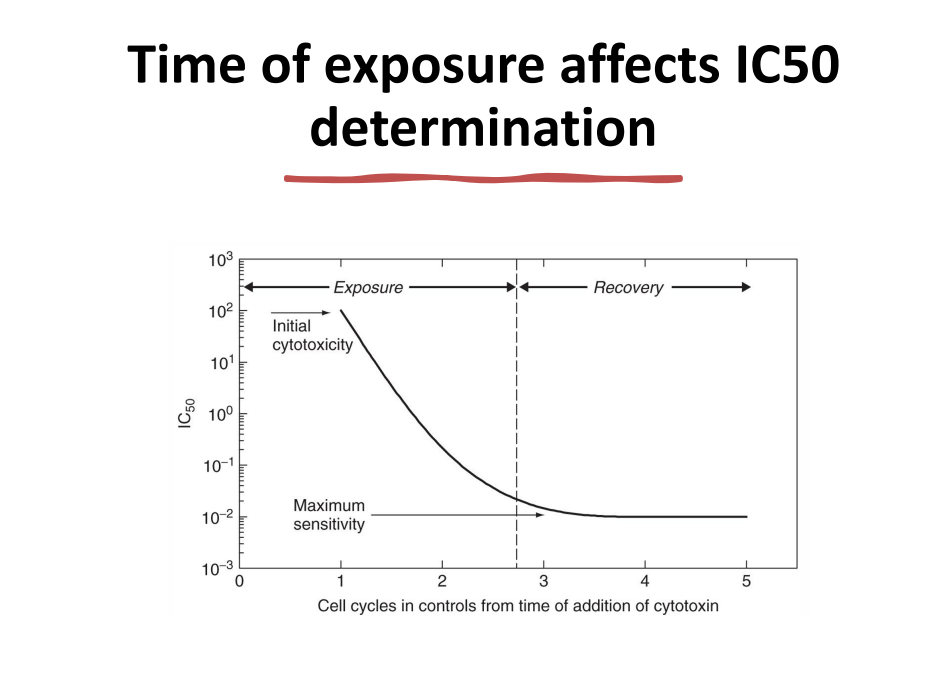
- duration of exposure
- time of exposure
- cell density during exposure
- medium constituents
- solvents
- survival curve
- IC50
- graph determine cytotoxicity activity of drug/cytotoxin
- % control plot against drug concentration
- result in sigmoidal curve
- IC50 = concentration where 50% inhibition occurs
- lower IC50 higher potency 效力
- based on graph below, IC50 value @ x-axis = ?
- 50% of cell population will die at the ? concentration of drug

- Survival*
- 3D spheroids
- simple 3D aggregates typically generated from single cell types
- use for disease modelling
- pros: easy to generate, cost effective
- cons: difficult to maintain long term
- organoids
- complex organized 3D structures that recapitulate概括/similar to original organ
- use for disease modelling, regenerative medicine, drug discovery
- pros: multiple cells in culture, more closely mimic tissue
- cons: challenging to generate
Cryopreservation = cell freezing
- reason for cell freezing
- contamination by microbe
- cross contamination
- misidentification due to careless handling
- need for distribution to other users
- genotypic drift due to genetic instability
- phenotypic instability due to selection & dedifferentiation
- principle - minimize intracellular ice crystal formation & reduce cryogenic damage
- slow freezing, rapid thawing
- freeze cells slowly
- use hydrophilic cryoprotectant
- DMSO - sequester 隔离 water
- store at lowest possible temp
- thawing rapidly
- minimize ice crystal growth & generation of solute gradients formed as residual intracellular ice melts
- cell concentration
- survive freezing at high cell concentration
- when cryogenic damage - cause cells leaky
- reduce viability on thawing
- allow sufficient dilution of cryoprotectant at reseeding after thawing
- no need centrifuge
- freezing medium
- serum
- increase concentration to 40%, 50% or 100%
- media
- cryoprotectant*
- DMSO penetrate cell better
- 5-15% concentration
- may be toxic in hematopoietic cells
- induce cells to differentiate after thawing
- glycerol
- hematopoietic cells
- low risk to induce differentiation after thawing
- why cooling rate of frozen cells is not linear
- cells survive best cooled at 1°C/min, cooling rate influenced by
- ambient temp 环境温度
- cooling rate is proportional to the difference in temperature between ampoules & ambient air
- @ -70°C, cells cool rapidly to around -50°C
- rate falls off significantly after that
- can leave ampoules @ -70°C overnight then transfer to liquid nitrogen
- insulation 隔热
- plastic ampoule - safe & convenient
- made of polypropylene
- inexperienced user avoid glass ampoule
- risk of explosion when thawed
- if glass used, make sure perfectly sealed & use vapor phase cooling
- specific heat and volume of ampoule contents
- higher specific heat capacity, slower cooling rate
- larger volume of ampoule content, slower cooling rate
- latent heat absorption during freezing
- slower cooling rate
- Vitrification*
- ways to control cooling rate
- cotton wool & polystyrene foam boxes
- ampoule canes in tubular foam pipe insulation
- freezer neck plug
- freezing container
- controlled-rate programmable freezer
3D Culture* types, adv disadv, compare 2D 3D
- organ culture - multiple type & lineage
- whole organs/representative parts maintained as small fragments in culture
- retain intrinsic distribution of participating cells
- technique
- primary explant with gas-liquid interface
- on semisolid gel substrate of agar/clotted plasma/raft of microporous filter, lens paper/rayon supported on stainless steel grid
- allow gaseous & nutrient exchange
- retain spherical geometry
- liquid level too shallow - induce surface tension
- liquid level too deep - inhibit gaseous exchange
- filter well insert
- compare with cell culture
- organ culture @ gas-liquid
- cell culture immersed in solid substrates - outgrowth of cells - alter geometry
- organ culture maintain cellular associations
- cell culture use cells disaggregated enzymatic/mechanical - intrinsic distribution destructed
- organ culture no grow & differentiate - density limitation of cell proliferation, physical restriction of geometry
- cell culture grows & differentiates to reach confluency
- limitation
- no vascular system
- experimental analysis depends largely on histological techniques
- more difficult to prepare
- cannot be propagated - original donor
- study behavior of integrated tissues rather than isolated cells
- histotypic culture - one cell type & lineage
- propagated cell lines are grown alone to high cell density in 3D matrix
- techniques
- gel & sponge technique
- cell penetrate cellulose sponge facilitated by collagen coating
- collagen gel
- Matrigel
- spheroid
- culture in gyrator shaker
- cells reassociate into clusters
- form tissue-like structures
- rotating chamber system - Miniperm bioreactor
- cells proliferate in small compartment cylinder with medium in large compartment - high cell concentration
- cells & medium separated by semipermeable membrane
- slow rotation ensure mixing
- membrane can be changed w/o disturb cell
- hollow fiber
- medium + 5% CO2 pump thro centers of capillaries
- cells attach & grow at outside of capillary fibers
- gas & nutrient permeable on fiber surface support cell growth
- filter well inserts choice:
- cell + matrix + filter
- cell + matrix + filter + interactive cell @ underside filter
- cell + interactive cell + matrix + filter
- cell + matrix + filter + interactive cell @ underside filter with matrix
- allows cells @ very high density to proliferate
- organotypic culture - multiple type & lineage
- recombined cells of different lineages in experimental determined ratios & spatial relationships to recreate a component of the organ under study
- steps
- determine cell types
- isolation
- culture until reach desired cell no
- according to experimental determined ratios & spatial relationships
- culture cells with various techniques
- techniques
- filter well insert
- hollow tube/perfusion chamber
- component
- tissue cells - endothelial cells
- interactive cells - dermal fibroblasts in skin, smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, glial cells in neural constructs
- biodegradable scaffold to support structure - PGA, PLA, calcium phosphate
- matrix - collagen to coat scaffold, to enhance cellular attachment
- mechanical stress - tensile for muscle, compressive for cartilage & bone, pulsatile for blood vessels




Comments
Post a Comment