Lecture 2 Biology of Cultured Cells
Lecture 2 Biology of Cultured Cells
- Culture environment
- physiochemical constitution of medium
- incubation temp
- constitution of gas phase
- degree of contact with other cells
- nature of substrate in which the cells grow
- Cell adhesion molecules
- mediated by specific cell surface receptors
- cadherin
- Ca2+ dependent
- c-c
- adherens junctions or desmosomes→actin cytoskeleton
- signaling, structural roles
- c-c adhesion molecules
- Ca2+ independent
- NCAM homophilic in neural synapses
- ICAM heterophilic in immunological synapses
- integrin
- c-m
- interact with fibronectin, entactin, laminin & collagen via RGD seq
- transmembrane proteoglycan
- c-m
- interact with other proteoglycan or collagen not via RGD motif
- claudins & occludins
- tight junctions
- homophilic
- help establish cell polarity
- Cytoskeleton
- integrins + actin via linker protein↔reciprocal signaling between cell surface & nucleus
- cadherins + actin in adherens→cell shape & morphogenesis
- cadherins + intermediate in desmosome→structural & signaling
- microtubules
- ECM (collagen, laminin, fibronectin, hyaluronan, proteoglycan) allows
- attachment & spreading for cell proliferation
- specific interactions of cells with basement membrane/adjacent tissue cells
- enhance cell survival, proliferation & differentiation
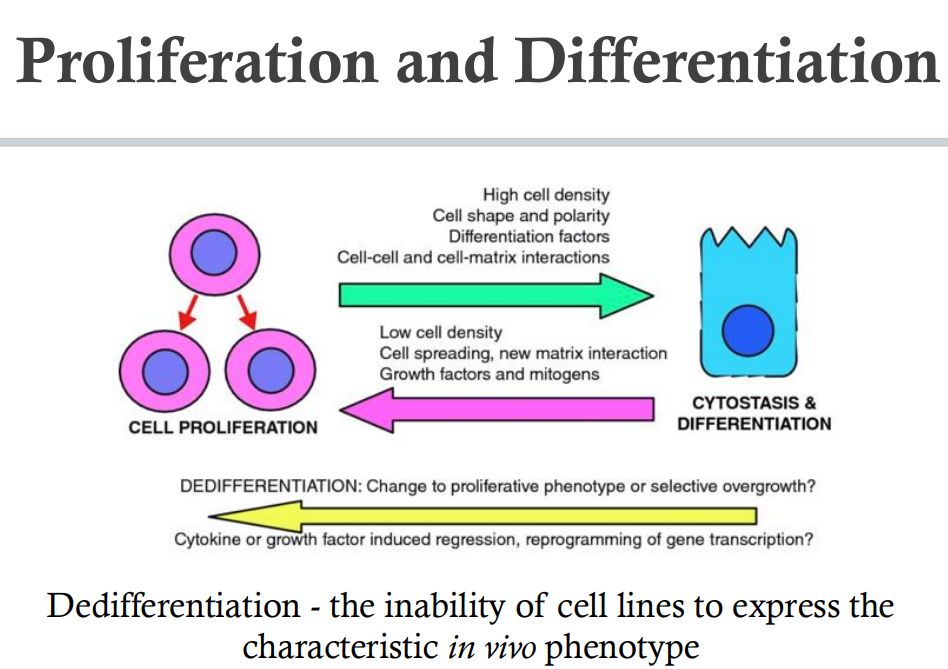
- Effects of new microenvironment
- lack heterogeneity & 3D architecture→absence of hormonal & nutritional stimuli; low c-c & c-m interaction
- favors spreading, migration, proliferation of unspecialized progenitor cells w/o differentiated function
- might not express correct in vivo phenotype
- Cell motility
- ruffling (edges of moving fibroblasts in culture repeatedly folded upward and inward)
- fibroblast exhibit high motility at low cell density
- dense epithelial monolayer show reduced motility
- contact inhibition→cessation of movement at confluence没位子, low PM ruffling, withdrawal of cells from division cycle
- Cell proliferation→G1, S, G2, M
- Cell signaling
- contact-mediated (cytoskeleton)
- diffusible factors
- autocrine→same cell
- homocrine→adjacent similar cell
- endocrine→insulin, glucocorticoid
- paracrine→heterotypic interaction of differ cells
- proliferation, migration, differentiation, apoptosis
- Energy metabolism
- glucose as main carbon source for glycolysis under anaerobic→generate lactic acid
- TCA remains active
- amino acid as carbon source
- deamination of glutamine produces ammonia
- use of dipeptides minimizes ammonia production
- Senescence
- normal cells can only divide a limited no of times
- die out after a fixed no of population doublings
- progressive shortening of terminal DNA seq in telomeres
- mutate gene p53 deletion (transformation)→continuous cell lines
- aneuploidy→transformed cells lose anchorage-dependance & often show some chromosome fragmentation


Comments
Post a Comment