Lecture 8 Preparation & Sterilization
Lecture 8 Preparation & Sterilization
- Sterilization
- cleaning
- All new apparatus, materials and instruments should be soaked in detergent overnight, thoroughly rinse and dried (do not expose materials that will corrode to detergent for > 30 min)
- Used items should be rinsed in tap water and immersed in detergent immediately after use, soak overnight, rinse in deionized water, dry in oven
- packaging→steam penetration, impermeable to dust, microbe, mite
- sterilization
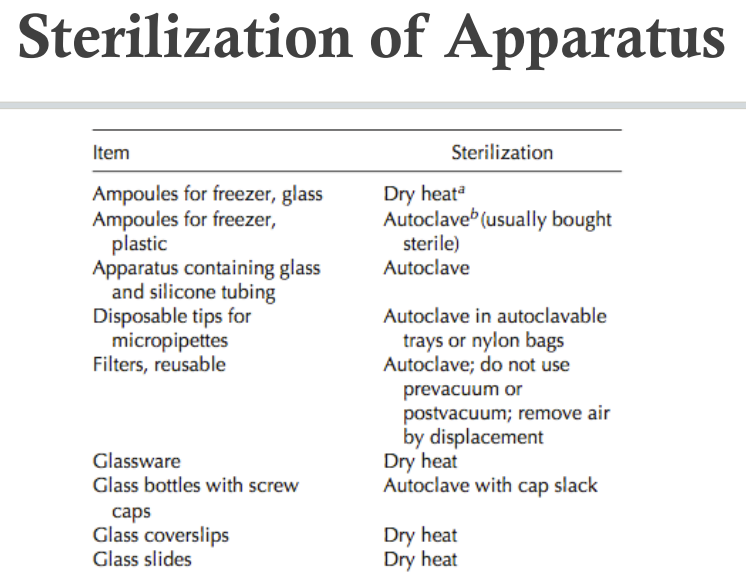
- metal→dry heat
- silicone rubber PTFE PCO3 cellulose acetate/nitrate filter→autoclave
- cleaning
- Methods
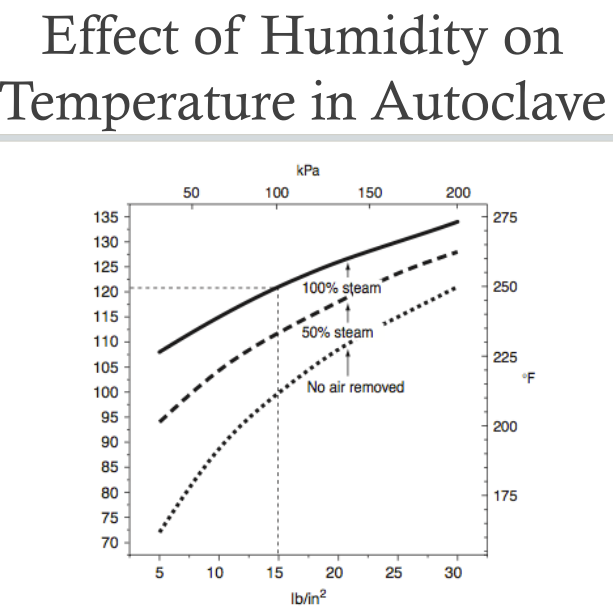
- dry heat→160C 1-2h
- moist heat→121C 20m
- glass
- moist heat with loose cap & autoclave tape, autoclave at 121C for 20m
- slack cap allow steam enter bottle and tighten it after cool down
- dry heat preferable
- thermalog indicator turns blue with high temp & steam→safe
- surface also need to carry correct charge for cell propagation
- caustic alkaline detergents render surface not suit for cell attachment→neutralize with 0.1M HCl/H2SO4
- detergent remove residue
- no toxic residue left behind to leach out into medium/reagent
- detergent→7X, MP Biomedicals, Decon
- Alternative
- Immerse in 70% alcohol for 30 min, dry them off under UV light in a laminar flow hood
- Ethylene oxide but 2-3 weeks are required to clear it completely from the plastic surface
- γ- irradiation at 25kGy

- Liquid sterilization
- avoid accidental inclusion of toxic substance
- enable reagent to be totally defined & fx of its constituents to be fully understood
- reduce risk of microbial contamination
- Reagents & media
- water purification
- 1 rinse glassware & reagent prepare→glass distillation, reverse osmosis
- 2 remove both organic & inorganic colloids→carbon filtration
- 3 remove ionized inorganic materials→high grade mixed bed deionization
- final removes microbe, trap resin may escaped from deionizer→micropore filtration
- ultrapure water if water is recycled continuously from micropore filter to reservoir
- water purification
- Media preparation
- commercial
- working strength solution 1x w or w/o glu→direct use
- 10x concentrates w/o NaCO3 & glu→dilute first
- powder w/w/o NaCO3 & glu→cheapest, not sterile, 10x concentrates cost 2-3x powder media but save on sterilization, 1x media most expensive & convenient
- adjust pH→alkali neutralize 10x concentrated medium
- +NaCO3→stable equilibrium with atmospheric CO2
- addition to medium→glu is unstable
- QC→check by incubate aliquot of complete medium at 37C for 48h before use
- commercial
- Media sterilization
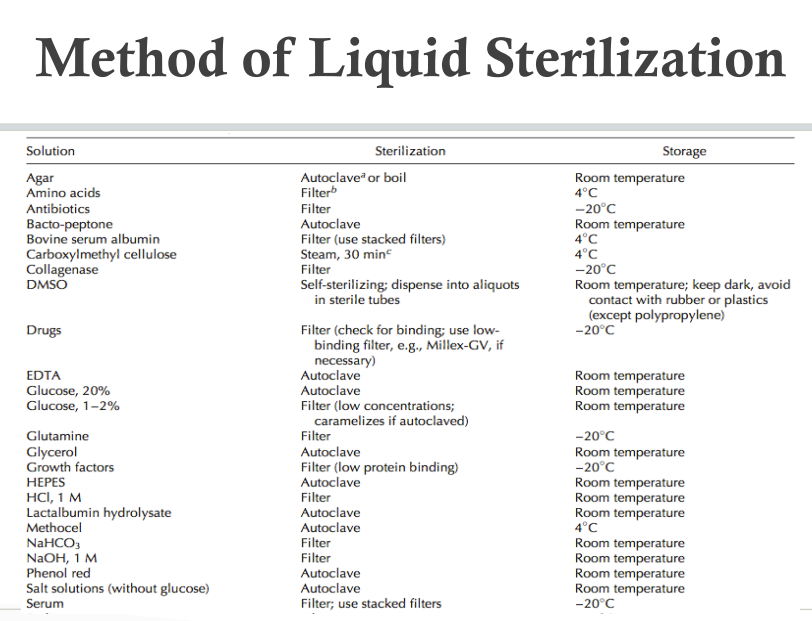
- autoclave
- less labor intensive, less expensive, low failure
- buffer pH 4.25 with succinate to stabilize VB
- glu replaced by glutamate/glutamyl dipeptide/added sterile after autoclave
- sterile filtration
- for heat labile solution
- filter thro 0.1-0.2 um PES, PCO3, PTFE, cellulose acetate
- -+pressure from a pressurized container/peristaltic pump
- in-line + peristaltic pump 100L
- bottle-top + vacuum pump 10L
- large scale 100-10kL
- autoclave


Comments
Post a Comment