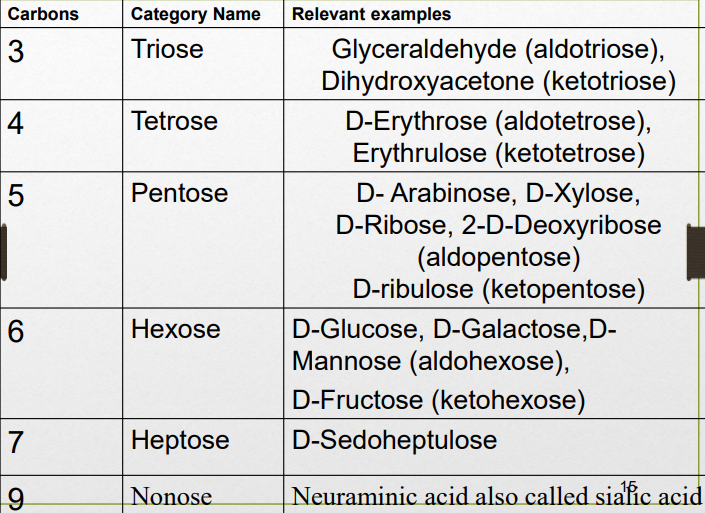
Carb
- Define carbohydrate
- hydrated carbon
- (CH2O)n≥3
- basic units: monosaccharides
- source from gluconeogenesis, photosynthesis
- Functions of carbohydrate
- carbon source
- energy source
- temporary stores of glucose
- structural and supportive elements
- components of cell membranes and CT
- antigenicity and anticoagulant
- lubricate skeletal & adhesive
- Classification of carbohydrate
- Monosaccharides
- Oligosaccharides (Disaccharide and trisaccharide)
- Polysaccharides
- Monosaccharide
- families/class→aldoses (carbonyl at end) & ketoses
- colorless
- crystalline solids
- free soluble in water but insoluble in nonpolar solvent
- sweet taste
- (CH2O)n=3
- D = OH on the right; L = left
- isomer aldohexose 6c=4 chiral carbon=2⁴=16 stereoisomer
- enantiomer→isomer that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
- ibuprofen→mixture of isomer
- epimer→isomer differ in configuration of OH and H on C2, 3, 4 of glucose vs galactose
- Haworth projection (ring, hemiacetal)
- pyran→6
- furan→5
- cis (beta)→OH up
- trans (alpha)→OH down
- Cyclic Fischer projection
- Define glycoside
- monosaccharides link together→glycoside bond/linkage
- monosaccharide hemiacetal + 2nd molecule of alcohol→acetal
- alkyl/aryl group + O2→B-D-glucopyranoside, a-D-ribofuranoside
- Derivatives of monosaccharide
- N-glycoside (ATCGU)→anomeric carbon (c-O2) of cyclic hemiacetal +NH group of amine
- toxic glycoside
- ouabain (African shrub) inhibit Na K pump
- amygdalin (bitter almond) yields (release) hydrogen cyanide on hydrolysis
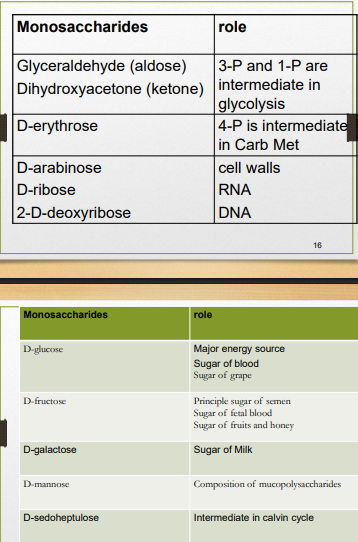
- reduction to alditols
- carbonyl group reduced to OH by H2 & Ni catalyst
- glucose to sorbitol for DM
- oxidation to aldonic acids
- B-D-glucopyranose to D-gluconic acid
- VC (ascorbic acid)
- for dentine, cartilage, CT, bone
- 45mg for adults, 60mg if pregnant, 80mg if lactating
- L-ascorbic acid synthesized biochemically & industrially from D-glucose
- B-D-glucopyranose to L-ascorbic acid
- very easily oxidized to L-dehydroascorbic acid (physio active, found in most body fluids)
- Glucose assay
- Disaccharide
- 2 monosaccharide
- maltose
- energy source (maltase)
- blood sugar regulation
- glycogen synthesis: store in liver & muscle; energy reserve for fasting/increased energy demands
- alpha OH在下
- beta (malt, barley, cereal)→major degradation product of starch
- 2 glucose + a(1,4) glycosidic bond
- lactose
- energy source
- calcium absorption
- maintain gut microbiota→prebiotic promote growth of beneficial bacteria which ferment lactose, produce SCFAs (acetate, propionate, butyrate)
- development of intestinal enzyme (lactase)
- 5-8% human milk; 4-5% cow milk
- galactose + glucose + B(1,4) glycosidic bond
- D-galactopyranose + D-glucopyranose
- lactose intolerance
- primary deficiency of lactase production in small bowel
- secondary to injury to intestinal mucosa
- lactose not absorbed, converted by colonic bacteria to lactic acid, methane gas, H2
- sucrose
- sugar cane, beets, table sugar, saccharose
- glucose + fructose + a(1,2) glycosidic bond
- B-D-glucopyranose + B-D-fructofuranose
- Homopolysaccharide
- starch
- 15-20% a-amylose
- D-glucose + a(1,4)
- 80-85% amylopectin
- 24-30 D-glucose+ a(1,4) bond + a(1,6) branch
- glycogen
- human starch
- similar to amylopectin
- location→7% liver, 1-2% muscle, RBC, kidneys, glial cells in brain, WBC, uterus, stomach
- glucose + a(1,4) linkage with a(1,6) branch every 8-10 residues
- cellulose
- linear, unbranch D-glucose + B(1,4)
- chitin
- B(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine polymer
- N-acetyl grp at C2
- structural polysaccharide of invertebrates (exoskeleton), cell walls of fungi and algae
- Heteropolysaccharide
- GAGs
- most abundant
- long unbranched contain repeating disaccharide with negative charge grp contain 2 modified sugars→N-acetyl galactosamine/N-acetylglucosamine & uronic acid (glucuronate & iduronate)
- N-acetyl-D-galacto/glucosamine + uronic acid (glucuronate/iduronate)
- location→EC space, vitreous humor of eye, synovial fluid of joints, CT
- subgroups
- hyaluronate
- copolymer of N-glucuronic acid & N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
- synovial fluid, inside of eye, IC matrix
- B(1,4) linked glucuronic & B(1,3) N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
- chondroitin sulfate
- CT, cartilage
- loss of chondroitin sulfate→osteoarthritis
- D-glucuronic acid & N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
- dietary supplement
- heparin
- glucuronic acid
- iduronic acid
- anticoagulant activate antithrombin 3 block thrombin
- DVT, pulmonary emboli
- keratan sulfate
- cornea 10-fold>CT
- cartilage, bone
- large highly hydrated molecules
- cushion to absorb mechanical shock
- basic repeating disaccharide→3Gal B(1,4)GlcNAc B1
- hyaluronate
- Mucopolysaccharidosis MPS
- intra lysosomal accumulation
- increase urine GAG
- autosomal recessive
- MPS 1
- Hurler-Scheie
- accumulated metabolites→dermatan sulfate & heparan sulfate
- deficiency of a-L-iduronidase
- most severe
- hallmark→coarse facies, corneal clouding, mental retardation, hernias, dysostosis multiplex, hepatosplenomegaly
- MPS 2 Hunter→dermatan sulfate & heparan sulfate
- MPS 3ABCD Sanfilippo→heparan sulfate
- MPS 4 Morquio→keratan sulfate
- MPS 5 Maroteaux-Lamy→dermatan sulfate
- MPS 7 Sly→dermatan sulfate & heparan sulfate & chondroitin
- MPS 1
- proteoglycans
- heavily glycosylated glycoproteins
- core protein with >1 C=C GAG chain
- long, linear, negative charge due to sulfate & uronic acid
- glycoproteins
- cell recognition/adhesion
- outer surface of human cells
- antifreeze protein = tripeptide Ala-Ala-Thr 50x in artic, antarctic fish
- hormones→FSH, LH, TSH, HcG, alpha fetoprotein, erythropoietin
- GAGs
- Coagulation
- factor→serine protease
- cleave proteins at specific sites
- cofactors for cascade→Ca, phospholipid, VK


Comments
Post a Comment