Lipid
- Define lipid
- not polymer
- small molecules
- have strong tendency to associate thro noncovalent forces→ionic, H, Van der Waals, hydrophobic
- Functions
- lipid signaling
- provide better absorption for vitamin
- provide efficient thermal insulator
- serves to cushion organs against shock
- energy storage
- basic building blocks of bio/lipid membrane
- Simple lipids
- FA
- monocarboxylic acid with hydrocarbon chains
- key components of lipid
- metabolic fuels
- oxidation of FA yields more energy than protein
- C16 & C18→0~3 double bonds
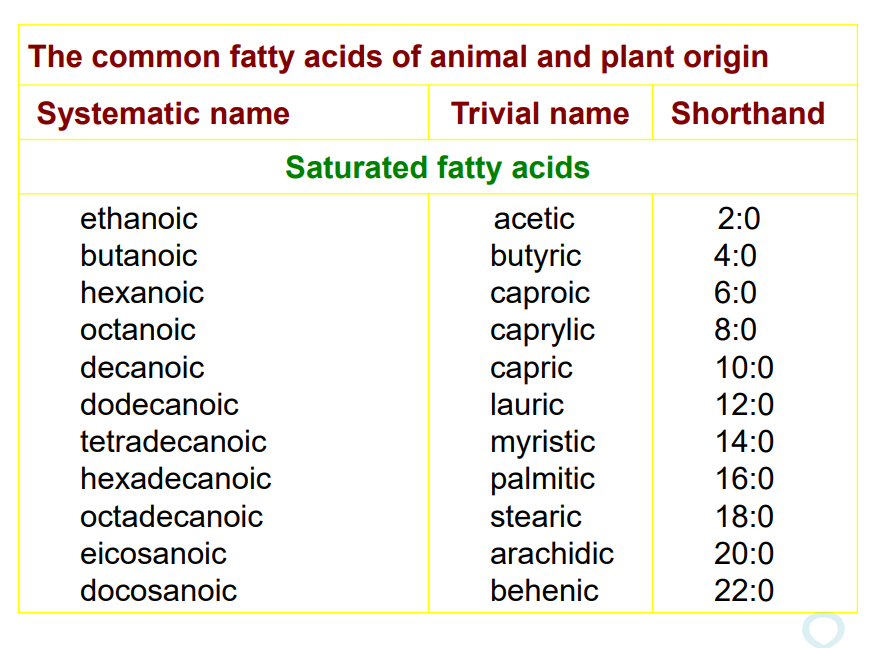
- CnH2n+1COOH
- butyric acid C3H7COOH in butter
- most abundant saturated→palmitic acid CH3(CH2)14COOH 16:0
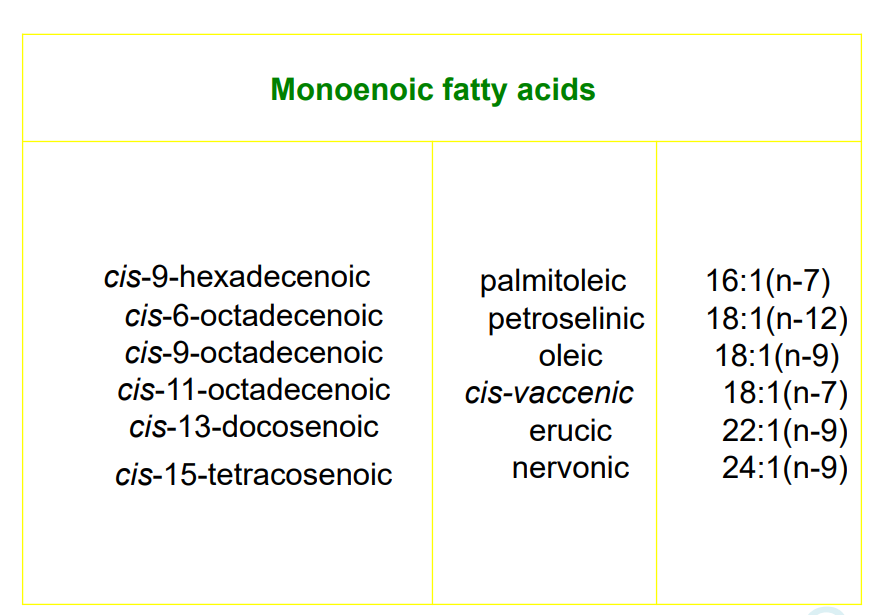
- most abundant monoenoic→oleic acid CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH 18:1
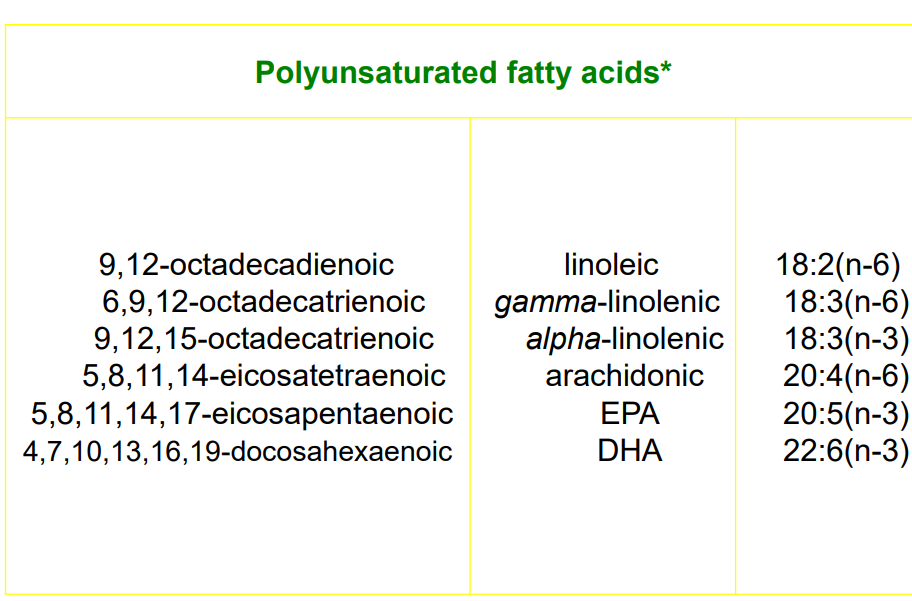
- human→PUFA with methylene interrupted double bonds of cis
- major component of C18 PUFA
- linoleic acid→cannot synthesized in human
- linolenic acid in food
- both precursor of C20 & C22
- arachidonic acid
- phospholipid
- precursor of prostaglandin & eicosanoid
- 4 double bond between c5-6, 8-9, 11-12, 14-15
- 20:4(n-6)
- prostaglandin
- unsaturated of 20 carbons, 4 double bonds, 5-member ring
- seminal fluid
- smooth muscle
- precursor→arachidonic acid PGA,B,D,E,F
- aspirin inhibit biosynthesis of prostaglandin
- nervonic acid, cis DHA→nervous system
- gamma linolenic acid→EPO 18:3(n-6)
- conjugated linoleic acid→9 cis 11 trans octadecadienoate
- TAG
- esterification of glycerol moiety with OH
- derived from diet, de novo synthesis in liver, storage depots in adipocytes
- neutral fats
- may contain unsaturated (oil, liquid at room temp), saturated (fat, solid at room temp) or mixed
- less oxidized than carb
- release more energy
- poor heat conductor, prevent heat loss
- store energy more efficiently than glycogen→glycogen + H2O
- adipocyte store TAG
- major storage & transport FA
- hydrophobic, coalesce into compact anhydrous droplets
- insoluble in aqueous→bile salt synthesized in liver & stored in gallbladder
- simple TAG
- tristearin→3 residues of stearic acid
- tripalmitin→animal fat, 3 residues of palmitic acid
- triolein→olive oil, 3 oleic acid residues
- mixed TAG
- stearo-oleo-palmitin
- glycerol + stearic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid
- DAG
- 2 moles of FA per mole of glycerol
- key cellular mssger
- rarely present at greater than trace levels
- intermediate in biosynthesis of TAG and other lipids
- generated on hydrolysis of PI by phospholipase C
- monoacylglycerol
- one mole of FA per mole of glycerol
- intermediate of enzymatic hydrolysis of TAG
- positional isomer=powerful surfactant
- wax
- FA esterified to long chain alcohol
- saturated/1 double bond
- weak hydrophilic
- water insoluble
- energy storage, waterproof, self-cleaning (ear), eco location, water repellent, lubrication, protective coat, hair conditioning(sebum)
- FA
- Complex lipids
- phospholipid
- hydrophobic domain→hydrocarbon chains of FA
- hydrophilic domain (polar head)→P
- bilayer, amphipathic
- emulsify agent
- surface active agent
- lowers surface tension of liquid to spread out over surface
- types
- phosphoglyceride
- glycerol, FA, P, alcohol
- cell membrane
- glycerophospholipid→blood lipoprotein, bile, lung surfactant
- source of PUFA→arachidonic acid
- types
- phosphatidic acid→glycerol 3 phosphate (polar) esterified with 2 FA (nonpolar)
- PC PE neutral phospholipid
- phosphatidylethanolamine 2nd most abundant
- phosphatidylcholine→reservoir of membrane bound arachidonic acid for eicosanoid synthesis
- PS PI acidic
- phosphatidylserine protect brain cells
- phosphatidyl inositol for signal transduction, anchor that tether protein to surface of PM
- sphingolipid
- sphingosine, FA, P, alcohol
- abundant in CNS
- IC comm
- antigenic determinant of ABO
- receptor by virus & bacterial toxin
- form myelin sheath
- signal transduction
- structural bone→sphingosine, unbranched C18 alcohol with trans double bond between C4 & 5, amino at C2, OH at C1 & 3
- basic unit
- ceramide=N-acylsphingosine
- long chain FA + amino of sphingosine
- + PC = sphingomyelin
- 4 class
- sphingomyelin (P)
- PC + C1 OH ceramide
- myelin sheath→successive wrappings of cell membrane of specialized myelinating cells around nerve cell axon
- facilitate rapid transmission of nerve impulse
- cerebroside & ganglioside (glycosphingolipid)
- saccharide head
- glycosphingolipid
- membrane of brain & nerve cells
- cerebroside
- 1 monosaccharide + beta glycosidic + C1 of ceramide
- galactocerebroside abundant in nerve tissue
- 15% of lipids of myelin sheath
- ganglioside
- more complex glycosphingolipid
- oligosaccharide contain N-acetylneuraminic acid (blue) + ceramide
- GM2→2nd monosialo/NeuNac residue
- sulfatide
- globoside
- sphingomyelin (P)
- sphingolipid storage ds
- hereditary deficiency of beta hexosaminidase A that degrade ganglioside G→Tay-Sachs=sphingolipidoses
- cell swell & die
- blind, muscle weakness, seizure, mental retardation
- phosphoglyceride
- isoprenoid
- 5C
- terpene
- plant essential oil
- monoterpene→2 isoprene, geraniol in geranium oil
- sesquiterpene→3 isoprene farnesene in cironella oil
- diterpene→phytol
- triterpene→squalene in shark liver oil & olive oil
- tetraterpene→carotenoid (orange pigment)
- polyterpene
- mixed terpene→VE, ubiquinone, VK, cytokinis, plant hormone
- steroid
- complex derivative of triterpene
- 4 fused rings
- cholesterol
- tetracyclic ring with double bond in one of the ring & 1 free OH
- maintain membrane fluidity
- esterified form
- precursor of 5 class of steroid hormone
- glucocorticoid
- mineralcorticid
- androgen
- estrogen
- progestin
- serum albumin→nonspecific carrier for steroid hormone
- plant sterol
- cardiac glycoside
- toxic
- ouabain from Strophanthus gratus seed
- digitalis from Digitalis purpurea→cardiac muscle contraction for congestive heart failure treatment
- lipoprotein
- protein covalently linked to lipid
- plasma a
- transport lipid molecules thro bloodstream
- lipid soluble antioxidant→a-tocopherol, carotenoid
- protein component of lipoprotein→apolipoprotein/apoprotein
- spherical, hydrophobic & apolar aa form inner core, hydrophilic & polar head outside
- classification
- chylomicron
- largest, most diameter
- deliver TAG from intestine via lymph & blood to muscle & adipose
- deliver cholesterol to liver
- LDL
- deliver cholesterol to nonhepatic cells
- enter cell by endocytosis after fuse with receptor then fuse with lysosome
- HDL most dense
- familial hypercholesterolemia
- lack LDL receptor
- prevalence 1:100, male 45.5% female 54.5%
- chylomicron
- phospholipid
- Eicosanoid
- precursor→arachidonic acid
- regulatory molecule
- local regulator
- thromboxane A2
- platelet aggregation, smooth muscle in arterial walls constrict
- cause localized change in blood flow
- mediate pain sensitivity, inflammation, swelling
- aspirin prevent formation of eicosanoid
- 4 class
- prostaglandin
- synthesized in prostate gland
- unstable, metabolized rapidly to inactive products
- no significant concentration in blood
- stimulate smooth muscle contraction of uterus→blood flow, pain, inflammation, fever, wake-sleep cycle
- thromboxane
- synthesized from platelet
- 6 member ring contains ester
- blood clot & decrease blood flow towards clot
- leukotriene
- synthesized in leukocyte
- 3 conjugated double bond
- acts as strong biological signals
- D4 cause smooth muscle contraction lines airway of lung
- adverse effect→asthmatic attack
- lipoxin
- lipoxygenase
- linear
- many OH
- cause anti inflammatory
- production enhanced in response to aspirin
- prostaglandin
- RDS
- deficiency in synthesis of lung surfactant
- dipalmitylPC→palmatate esterified to C1 & 2
- PG
- apoprotein
- cholesterol→reduce surface tension of fluid within alveoli preventing collapse
- AT1
- AT2
- premature infant→estimation of fetal head by ultrasonography, monitor fetal arterial O2 saturation, determine [PC] & [sphingomyelin] in amniotic fluid
- Alzheimer→3 allelic form apo E
- Atherosclerosis
- atheromas accumulate in arteries (plaque)
- calcify & protrude into arterial lumens
- disrupt vital organ functions→brain, heart lungs
- O2 & nutrient deprivation
- macrophage found within plaque
- high LDL
- VC VE antioxidant retard plaque
- Lipid signaling
- activation of nuclear receptor
- Cell growth
- sphingosine 1 phosphate→ceramide
- potent mssger
- regulate Ca mobilization, cell growth, apoptosis
- DAG & PIP→Ca mediated activation of protein kinase C
- Inflammation
- prostaglandin
- arachidonic acid
- estrogen, testosterone, cortisol
- oxysterol 25-hydroxy-cholesterol→LXR agonist
- fat soluble vitamin ADEK isoprene based lipid stored in liver & fatty tissue
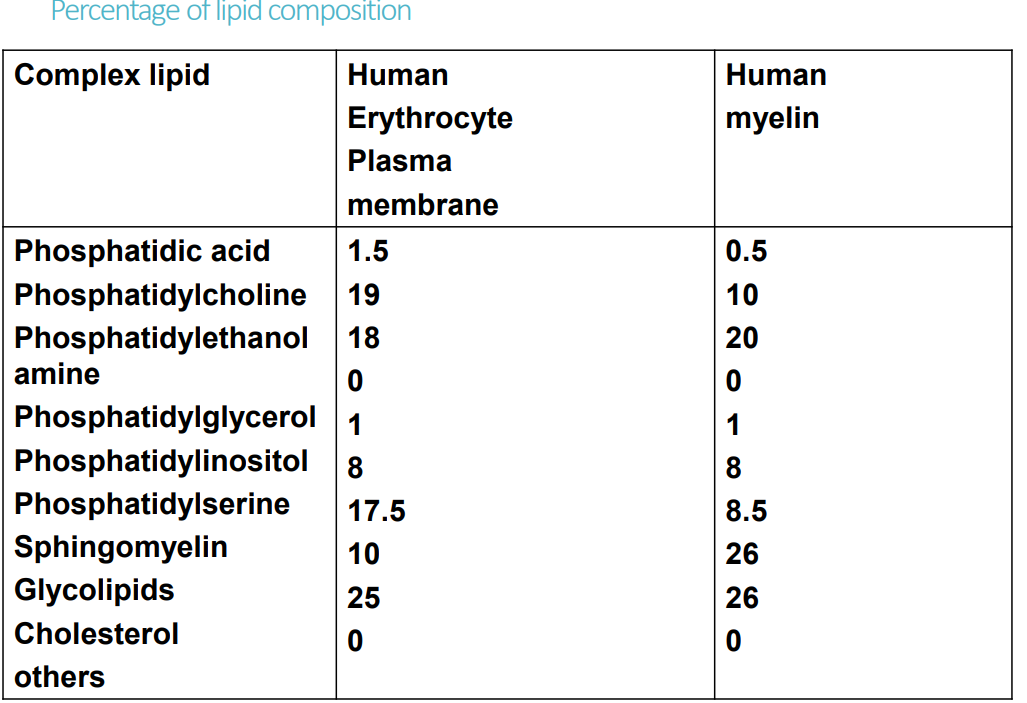
- Membrane
- highly polar head + 2 hydrocarbon tail
- 3 class→glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid, glycosphingolipid
- double tail yield cylindrical shape, easily packed in parallel
- hydrocarbon tail has FA
- unbranched 14-24 C chains connect by single bonds alone (saturated)/both single & double (unsaturated)
- micelles→tail inside, COOH water
- if mix with water & oily/greasy, micelle form oil droplet, emulsify
- soap, synthetic detergent action
- Lipid as energy reserve
- complete metabolic oxidation of TAG→37kJ per g
- carb & protein→17kJ per g
- 70 kg human→400k kJ in total body fat & 100k kJ in total protein (muscle)
- FA oxidation
- brain unable to use FA
- when starve & blood glucose low, brain use ketone bodies



Comments
Post a Comment