Protein
- Define protein
- 1/2 life < 1h (ornithine decarboxylase, phosphokinase C, insulin)
- 1/2 life several months (collagen, hemoglobin, histone)
- organism for the crystallin of the lens throughout life
- majority turn over every few days
- green fluorescent protein→Ser-Tyr-Glycine
- all polymer
- monomer a-aa
- peptide bond
- Amino acid structure
- a-carbon→c next to COOH carboxyl
- amino group + a-carbon→a-amino acid m
- side chain (R)
- H atom
- L-aa
- D-sugar→DNA, RNA
- D-aa exist but L-isomer preferred→Ala
- 2 stereoisomer/enantiomer (2N)→a molecule contains 1 asymmetric carbon
- Glycine
- nonpolar aa
- simplest
- R is H→2 groups on a-carbon are same, eliminate chirality
- not optically active as 2nd H atom at a-carbon
- can fit into many places with small side chain (internal aa of collagen helix)
- very evolutionary stable (cytochrome c, myoglobin, hemoglobin)
- mutation to larger R chain can break protein structure
- collagen has 1/3 glycine
- 2 non standard amino acid
- pyrrolysine produce methane & code for UAG
- selenocysteine code for UGA
- Amino acid class based on structure
- aliphatic = non aromatic hydrocarbon
- aromatic
- heterocyclic→>1 ring member not carbon atom
- cyclic aa
- imino acid: proline→secondary amino group
- nonpolar
- found in 1st residue of a-helix, edge strand of b-sheet
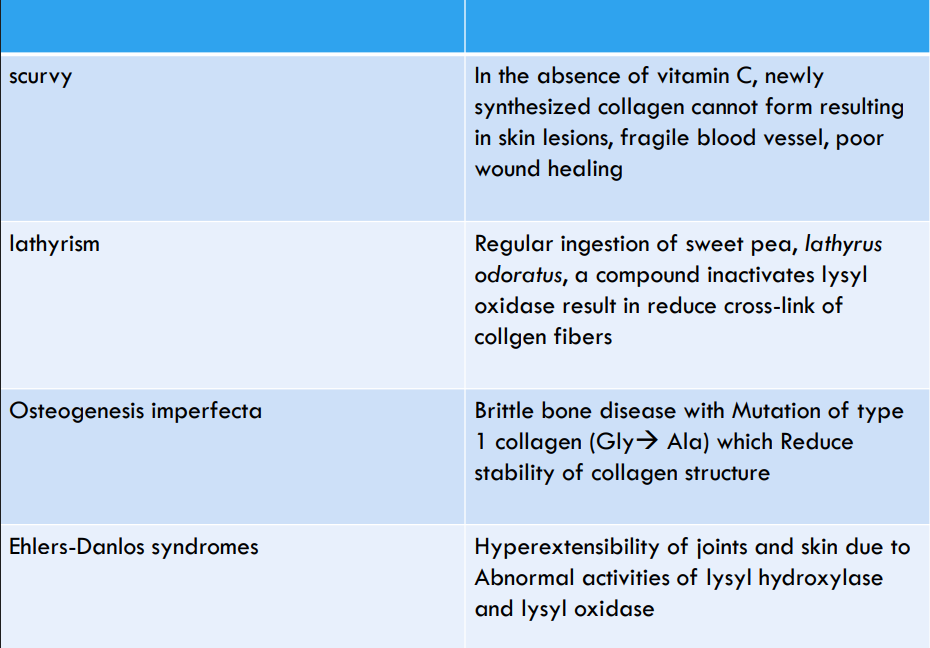
- ascorbic acid as cofactor for prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase
- hydroxyproline hydroxylysine stabilize collagen
- scurvy→mutation in prolyl hydroxylase/lack ascorbate cofactor, defect in hydroxylation
- simple aa (Simple GAla)→glycine, alanine
- branched aa (Branched VIaL)→valine, leucine, isoleucine
- hydroxyl aa (SeT OH)→serine, threonine
- Sulphur aa (Maple Syrup Cake)→cysteine, met
- amide group in aa (AG)→asparagine, glutamine
- special group in aa
- arginine - guanidine
- phenylalanine - benzene
- tyrosine - phenol
- trp - indole
- histidine - imidazole
- proline - pyrrolidine
- acidic aa (NH2 + 2 COOH)→aspartic acid, glutamic acid
- basic aa (1 COOH) (Basic HAL)→lysine, arginine, histidine
- histidine
- boost histamine levels when + B3 niacin & B6 pyridoxine
- convert into histamine for sexual functioning
- low levels contribute to RA & deafness as nerve damage
- high levels link to anxiety & schizophrenia
- myelin sheath
- aromatic aa
- absorb UV
- non polar
- tyrosine→semi-essential, synthesized only from phenylalanine
- phenylalanine→from diet
- PKU
- genetic ds
- mutation in gene of hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase which metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine (lack enzyme)
- enzyme activity reduce, phenylalanine accumulate & convert into phenylpyruvate/phenyl ketone in urine
- complications: mental retardation, seizures
- trp
- from diet
- precursor for serotonin (neurotransmitter), melatonin (neurohormone), niacin
- functional group is indole
- Amino acid class based on side chain
- nonpolar (Trp VIP LAMP)→ala, val, leu, ile, met, pro, phe, trp
- polar, hydrophilic (SeT CysT GAs)→ser, thr, cys, tyr, gln, asn
- ionic→negative charge=acidic aa; positive=basic aa
- Amino acid class based on metabolic rate
- purely ketogenic→leu
- ketogenic & glucogenic (PITTLy)→lys, ile, phe, tyr, trp
- purely glucogenic (Met His Valentine 3G4AS PCT)→arg, glu, gln, his, asp, pro, val, threo, met, asn, ala, cys, gly, ser
- Amino acid class based on nutritional requirements
- essential for growth, x be synthesized, from diet (PVT TIM LL)→ile, leu, thr, lys, met, phe, trp, val
- semi-essential (HA)→his, arg
- nonessential (3G3AS PCT)→gly, ala, ser, cys, pro, tyr, asp, glu, asn, gln
- Amino acid properties
- sweet (His GAS PVT)→gly, ala, val, ser, trp, his, pro
- tasteless→leu
- bitter→ile, arg
- all high melting point >200
- all soluble in water & alcohol (polar solvents)
- all insoluble in nonpolar solvents (benzene)
- Derivatives of amino acid
- flavoring→MSG
- sweetener→aspartamine (asp & phe)
- found in protein→OH pro, OH lys
- not seen in protein→ornithine, citrulline, homocysteine, thyroxine
- non a-aa→GABA from glutamic acid, B-alanine
- 5 HTP treat PKU, depression (alternative to L-trp)
- L-DOPA treat Parkinson
- Iso-electric point
- protein no net charge
- cation in acid→amide group protonated
- anion in alkaline→carboxyl group deprotonated
- aa as ampholytes/zwitterions depend on pH
- zwitterion
- active groups (R) of an amide & carboxylic acid→acid and base
- white crystalline with very high melting point due to dipolar nature
- Reaction to carboxyl group
- decarboxylation→hist-histamine + CO2, tyr, trp, lys, GABA
- amide formation (COOH + NH3)→asp-asn, glu-gln
- Peptide formation→CO-NH bridge
- Protein functions
- transport small molecules
- storage
- structural framework
- muscle contraction
- immune response
- blood clot
- enzyme
- catalyst
- genetic
- contractile
- hormone
- Protein structure
- proteios→primary
- CHON, minor SP
- N2 16% by weight
- Globular
- Soluble in aqueous medium
- Resemble irregular balls
- Fibrous
- Linear in single axis with repeating unit
- DNA binding
- Inducer + repressor = DNA expression
- Corepressor + repressor + operator = prevent gene transcription
- Membrane
- Integral + hydrophobic + membrane-lipid
- Free by denaturating condition/detergent SDS
- Amphiphile
- Peripheral
- Do not bind lipid
- Cytochrome c outer surface of inner mitochondrial membrane
- Lipid linked
- Attach to isoprenoid/FA
- C15 farnesyl C20 geranylgeranyl
- C14 myristic acid C15 palmitic acid
- Levels of protein structure
- primary
- straight chain, covalent bond peptide linkage
- disulfide bridge→chains bond together with 2 S
- secondary
- regions within polypeptide chains from recurring, localized structures
- configurational relationship between residues 3-4 aa apart in linear seq
- a helix & b sheet VIPTTT
- loops & coils→nonregular nonrepetitive
- super secondary
- a helix + b sheet
- reverse turns allow a & b align side by side
- glycine small size allows a turn
- proline geometry favors a turn
- tertiary
- 3D, hydrophobic, E, Van Der Waals forces
- quaternary
- polypeptide aggregate to form 1 functional protein
- >1 polypeptide chain (Hb, CK, LDH, aspartate transcarbamoylase)
- primary
- Leptin
- 4 antiparallel helices, 5-6 turn long
- 2 long loop connect helices a-b & c-d, shorter loop connect helices b-c
- Bonds
- H
- relatively weak in aqueous, large no for stability
- sharing H between 2 electron donor
- H releasing→NH(imidazole, indole, peptide) OH NH2
- H accepting→COO C=O(peptide) S-S
- electrostatic (E)
- between + - side chain group
- +→epsilon amino group of lys, guanidinium group of arg, imidazolium group of his
- -→beta & gamma carboxyl group of asp & glu
- hydrophobic
- between nonpolar hydrophobic side chain
- eliminate H2O
- hold lipophilic side chains together
- Van der waal
- weak between uncharged group but contribute max to stability
- H
- Disulfide bond S-S
- bovine pancreatic trypsin→most stable protein
- inert to unfolding reagents→urea
- exhibit thermal denaturation <100C in very acidic solutions
- 1/2 point for reversible denaturation 80C at pH2.1
- rare, found in ribonucleases & insulin
- environment in cells is reducing→Sulfhydryl group (R-SH) in reduced state
- external environment is oxidizing→stabilize S-S
- Hb
- O2 transport
- remove metabolic waste CO2
- protein chains in developing RBC remain for life
- identical in AB blood
- gamma (fetus)→a & b (adults) differ gene number but equal amount
- tetrameric protein
- Myoglobin
- single polypeptide chain folded about a prosthetic group heme with O2 binding site
- store O2
- monomeric heme protein
- 17000KDA molecular weight
- release from skeletal/cardiac when cell damage
- secondary→75% a helices
- tertiary→water soluble globular
- polypeptide→8 right handed a-helices, R hydrophobic inside, hydrophilic outside
- Heme
- iron (Fe2) chelated by tetrapyrrole ring system→protoporphyrin IX
- O2 with Fe2 oxidize ferrous ion to ferric
- metmyoglobin/methemoglobin
- P50 value
- RBC 50% saturated with O2
- oxyHb→RBC fully saturated with O2
- curve shift right→temp high pH low DPG high
- temperature→denature O2 & Hb bond, high O2 & Hb, decrease oxyHb concentration
- pH→acid by adding CO2, Bohr shift
- organic P→+Hb, rearrange HB into T state, decrease affinity of O2 for Hb (T & R)
- Hyperventilation→breathe too rapid, high O2
- Thalassemia→nonsense, loss/misfunction a & b chain
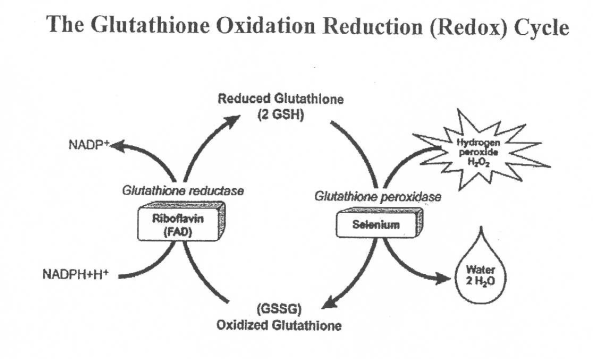
- Glutathione→tripeptide glu-cys-gly
- Plasma protein
- albumin most abundant, synthesized in liver
- oncotic pressure of plasma
- CLD
- acute hepatitis
- 3 homologous domains each with 2 subdomains & 5 or 6 internal S-S
- hydrophobic cavities
- regulate colloidal blood osmotic pressure
- + H2O, cation Ca Na K, FA, hormones, bilirubin, thyroxine T4, unconjugated bilirubin, drugs (barbiturate)
- hypoalbuminemia
- Low albumin high bilirubin
- Jaundice
- Kernicterus
- Treatment: salicylic acid
- Low renal blood flow high renin
- Vasoconstriction
- Na+ retention
- High capillary hydrostatic pressure low oncotic pressure
- Edema
- Crohn's disease (malabsorption)
- bisalbuminemia
- hyperalbuminemia
- Venous stasis
- Dehydration
- ECM protein
- structural protein→collagen, elastin
- specialized protein→fibrillin, fibronectin, laminin
- proteoglycan→core + long chain=GAG
- Collagen
- 1 bone tendon ligament skin
- 2 hyaline articular cartilage
- 3 mesh in soft tissue organ
- 4 placenta
- 5 cell surface hair cartilage
- primary→gly-pro-hyp repeat triplet
- secondary→left helical
- tertiary=secondary
- quaternary→3 chain form right superhelical
- Precipitation
- salt - ammonium sulphate, sodium sulphate
- organic solvent - ester, alcohol
- heavy metal - iron, copper, zinc, lead, cadmium, mercury
- anionic, alkaloidal reagent - tungstic acid, phosphotungstic acid, TCA, picric acid, sulphosalicylic acid, tannic acid
- Denaturation→heat, alcohol, urea, x ray, uv, high pressure, shaking, physico-chemi agents


Comments
Post a Comment